Blaník L13
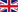
Wing/fuselage reinforcement
The outrage in the Blaník L13 community was enormous, after EASA grounded all airplanes in 2010. The cause for this drastic measure was a fatal in-flight wing rupture, whose cause was quickly identified by an FEM-analysis of the load path.
For regaining airworthiness of this Type, AD&C has developed a Supplemental Type Certificate, which improves the load path of the critical area.
5000 hrs useful life approved for Blanik L13 modification
Regaining airworthiness of Blanik L-13: STC ADxC-DC-39-001 or -004
Blaniks are/can be modified in the following countries:
- Austria
- Argentina
- Brazil (in preparation)
- Canada
- Czech Republik
- Germany
- Iceland
- Japan
- Slowenia
- Serbia
- USA (in process @FAA since one year)
A major change to the STC has been approved by EASA providing alternative limitations
You can now select between:
- NO aerobatics and life extension to 5000hrs useful life (ADxC-DC-39-004)
- Aerobatics and 3750hrs useful life (ADxC-DC-39-001)
STC revision 1 for 5000hrs useful life is approved by EASA on 28-Feb-2012 (see certificate here)
The STC has been approved as Method of Compliance in EASA AD 2011-0135
The STC is approved as Alternative Method of Compliance for the AD on 20-june-2011 (AMOC)
STC has been approved by EASA on 14-june-2011 (see certificate here)
STC for compliance with EASA-AD-2010-0185-E. Order form
Eligibility
Your aircraft can be modified according this STC when it has less than 3750hrs of operational time. Aerobatic use must be below 2% or if exceeded the TC-holder (Aircraft Industries) must be consulted for corrective actions before the STC is applied. The STC is applicable also for aircraft with unknown history but known exceedance of aerobatic use may have damaged your aircraft at areas not affected by the STC and must be corrected before.
The STC includes a structural modification as well as an inspection and replacement program. It is based on:
- Elaborate 3D geometry
- Load path analysis by reverse engineering
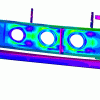
- Verification by FEM calculations and structural testing, including strain verification, up to individual rivet level
- KosMos (DLR) load spectra (cumulative exceedance and Markov matrix representation) used for analysis on wing and fuselage carry through sections, incorporating a realistic quantity of aerobatic maneuvers
- Analysis of wing root, wing section of fuselage and horizontal tail attachment area
- Crack propagation calculations using the AFGROW program, which is based on the USAF Damage tolerance design handbook
- Definition of useful life with and without (undetected) damage to substantiate appropriate but not unnecessarily short re-inspection intervals.
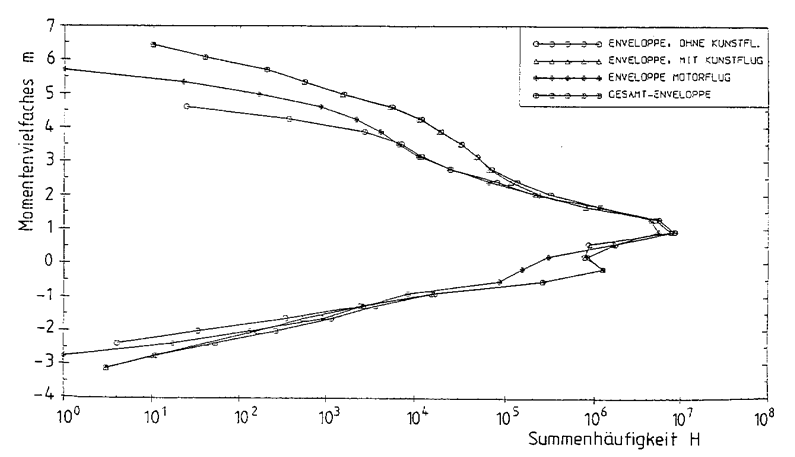
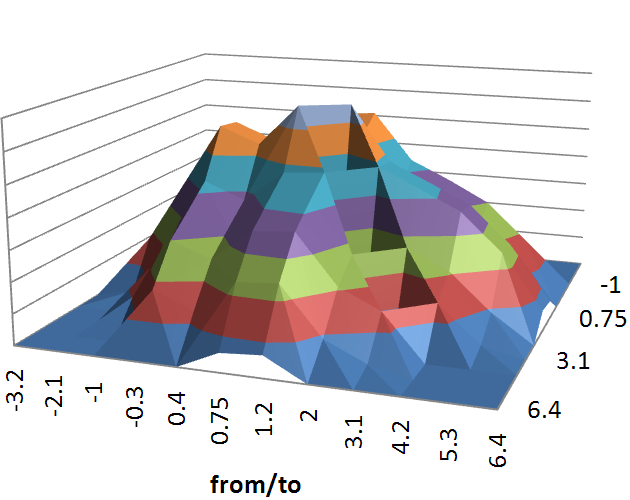
Modification
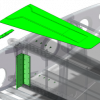
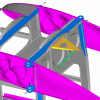
The modification consists of an additional root rib bracket, addition and replacement of several highly loaded rivets, and an additional girder plate attached to the spar at the lower wing root.
The parts are produced by CNC milling, for optimal precision and use of material.
The use of Hi-Lok fasteners ensures superior fatigue resistance and easier inspections in the affected areas.
Inspection Program
The inspection program addresses the overall airplane. Specific NDT inspections are mandatory during the structural modification and in increments thereafter.
The NDT inspections are made possible by definition and usage of a reference normal. A part taken from an original aircraft structure in which realistic cracks have been incorporated. With this approach AD&C was able to define a method that has a relative small undetectable crack size and helps to define the longer re-inspection intervals.